Dry etching
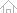
- Isotropic Etching
- Film etching only through a chemical reaction between film surface and radical
- Anisotropic etching through random mobility of radical
- High selectivity (chemical reaction)
- Low damage to the bottom layer
- Generation of undercut and difficulty with fine patterns
- Excessive use of chemicals leading to environmental problems
- Anisotropic etching
- Etching by a chemical reaction stimulated by ions accelerated by self-bias
- Almost no side erosion because of ions accelerated in one direction
- Superior etching resolution (1um or below)
- Damage to the bottom layer possible due to etching by physical impact
Dry etching Types
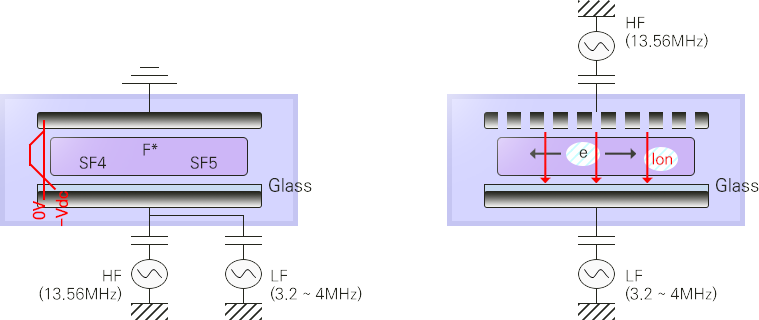
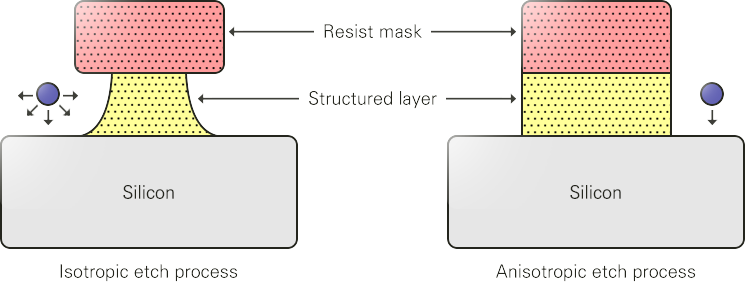
- ECCP
(Enhanced Capacitive Coupled Plasma) -
CCP (Capacitive Coupled Plasma) is a device for generating
plasma with the structure in which a dielectric is inserted
between parallel plates -
The plasma density is lower than the method of ICP
but can create uniform plasma in a relatively simple manner -
It is widely used for semiconductor device and thin film Si
solar cell manufacturing processes because large-surface
etching and deposition is possible
- ICP
(Inductive Coupled Plasma) -
The method of ICP (Inductive Coupled Plasma) allows
electricity to flow through a coil-shaped antenna located
outside a reactive chamber so that electrons are vibrated
in a horizontal direction via the electric field
around the antenna, which leads to higher electron density
than other plasma sources due to low absorption of electrons
by electrodes (high-density plasma) - Etching is done by attracting ions from a bottom bias electrode